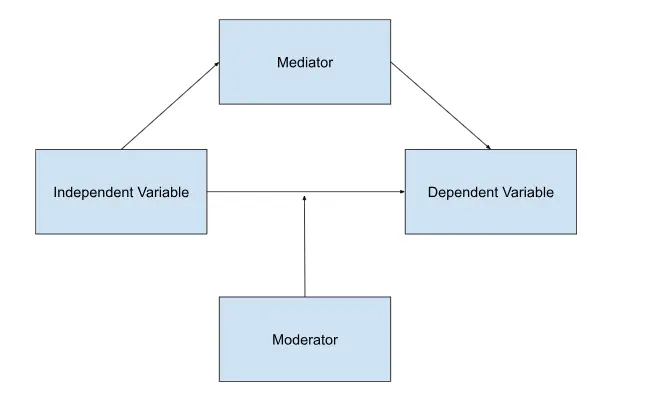
Mediators: These are intervening variables that explain the process of how an independent variable (IV) influences a dependent variable (DV). They act as the mechanism, clarifying how the IV impacts the DV.
Moderators: These are conditioning variables that alter the strength or direction of the relationship between the IV and DV. They act as the context, revealing under what conditions the effect of the IV on the DV is modified.
What Are Mediating Variables
Mediating variables play a crucial role in understanding the mechanism or process through which an independent variable influences a dependent variable. In simpler terms, they help to explain why or how the relationship between the independent and dependent variables exists.
Mediating variables are often referred to as intermediate variables or mechanisms in dissertations and research papers, because they mediate or intervene in the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. They provide insight into the underlying processes or pathways that link the variables of interest.
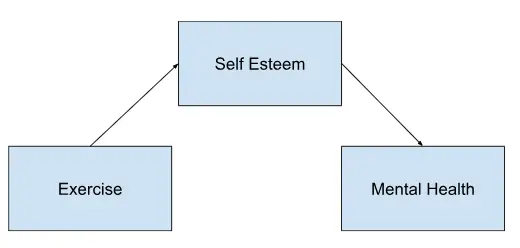
For example, let’s say we’re studying the relationship between exercise (independent variable) and mental health (dependent variable). A mediating variable in this scenario could be self-esteem. Through self-esteem, exercise may positively influence mental health by boosting confidence and reducing stress levels. Therefore, self-esteem acts as a mediator in explaining the relationship between exercise and mental health.
How Mediating Variables Work
Mediating variables operate by transmitting the effects of the independent variable to the dependent variable. They serve as a bridge or mechanism through which the influence of the independent variable is conveyed to the dependent variable in a thesis or dissertation.
In statistical terms, mediating variables are often tested using mediation analysis techniques. These techniques assess the indirect effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable through the mediator.
The strength and significance of the indirect effect help researchers determine the extent to which the mediating variable explains the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Mediating variables can operate through various mechanisms, including cognitive processes, emotional responses, physiological changes, or behavioural pathways. Understanding how these mechanisms function is essential for accurately identifying and interpreting mediating variables in research studies.
Examples Of Mediating Variables
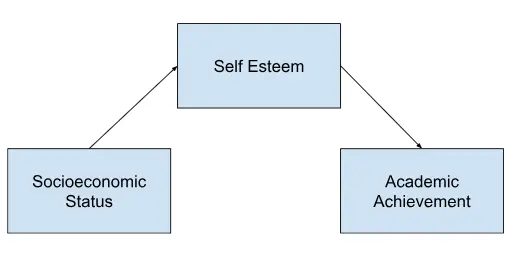
In a study investigating the relationship between socioeconomic status (independent variable) and academic achievement (dependent variable), the mediating variable could be parental involvement in education. Parental involvement may mediate the relationship between socioeconomic status and academic achievement by influencing factors such as parental support, access to educational resources, and motivation.
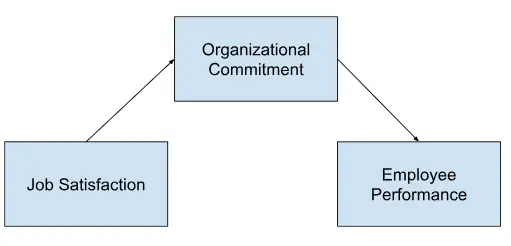
In research exploring the impact of job satisfaction (independent variable) on employee performance (dependent variable), a mediating variable could be organizational commitment. Organizational commitment may mediate the relationship by fostering greater engagement, loyalty, and effort among employees, thereby enhancing their performance.
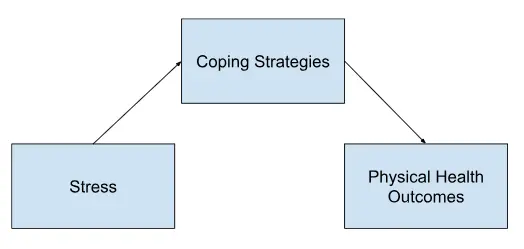
In a study examining the effects of stress (independent variable) on physical health outcomes (dependent variable), a mediating variable could be coping strategies. Coping strategies, such as problem-solving or seeking social support, may mediate the relationship by influencing the body’s physiological response to stress and buffering against its negative effects on health.
What Are Moderating Variables
Moderating variables, also known as interaction variables, serve to qualify or alter the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. Unlike mediating variables, which explain why or how a relationship exists, moderating variables influence the strength or direction of the relationship under different conditions.
In essence, moderating variables answer the question: “When does the relationship between the independent and dependent variables change?”
Moderating variables introduce variability into the relationship between the independent and dependent variables by affecting the conditions under which the relationship holds or differs. They can highlight the circumstances under which the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable are enhanced, attenuated, or even reversed.
How Moderating Variables Work
Moderating variables operate by altering the nature of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables across different levels or conditions of the moderating variable.
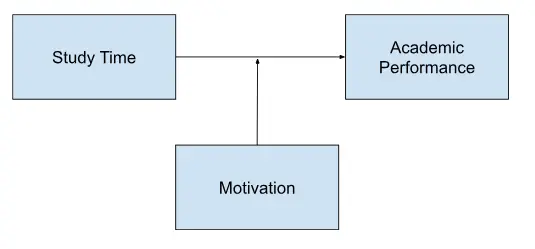
For instance, let’s consider a study examining the relationship between study time (independent variable) and academic performance (dependent variable), with motivation as a moderating variable. In this scenario, motivation may influence the strength of the relationship between study time and academic performance. Students with high motivation may demonstrate a stronger positive relationship between study time and performance compared to students with low motivation.
Moderating variables are often tested using interaction terms in statistical analyses, such as regression analysis. Interaction terms allow researchers to assess whether the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable varies depending on different levels or conditions of the moderating variable.
Examples of Moderating Variables
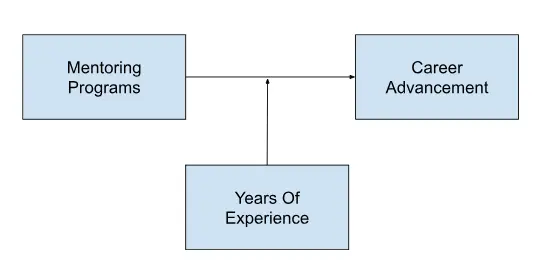
In research investigating the impact of mentoring programs (independent variable) on career advancement (dependent variable) among employees, years of experience could serve as a moderating variable.
The relationship between mentoring programs and career advancement may be stronger for employees with fewer years of experience, as they may benefit more from guidance and support compared to seasoned employees.
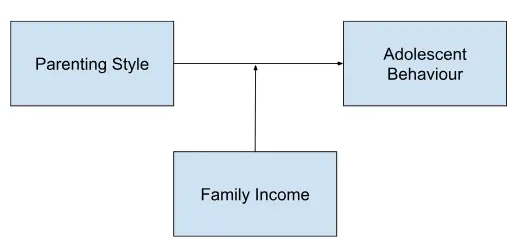
In a study exploring the effects of parenting style (independent variable) on adolescent behaviour (dependent variable), family income could act as a moderating variable. The relationship between parenting style and adolescent behaviour may differ based on different levels of family income.
For example, here is a hypothesis based on the above statement, authoritative parenting may have a more positive influence on behaviour among adolescents from higher-income families compared to those from lower-income families.
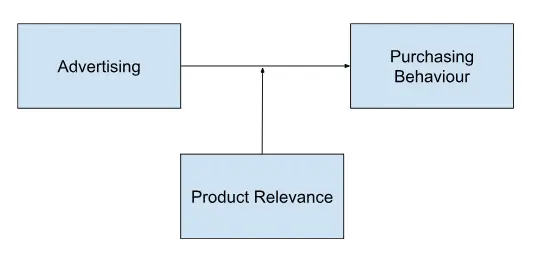
In research examining the impact of advertising (independent variable) on purchasing behaviour (dependent variable), product relevance could serve as a moderating variable.
The relationship between advertising and purchasing behaviour may be stronger for products that are highly relevant to consumers’ needs or desires compared to products with low relevance.
Key Differences Between Mediating Vs Moderating Variables
Mediating variables intervene in the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, explaining the underlying mechanism or process through which the independent variable affects the dependent variable. They provide insight into why or how the relationship exists and are often referred to as intermediate variables.
Moderating variables, on the other hand, qualify or alter the strength or direction of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables under different conditions. They influence the circumstances under which the relationship holds or differs, rather than explaining why or how it exists.
Function
The primary function of mediating variables is to elucidate the mechanism or process through which the independent variable influences the dependent variable. They help researchers understand the underlying pathways or intervening variables that transmit the effect of the independent variable to the dependent variable.
Moderating variables function to qualify or alter the relationship between the independent and dependent variables under different conditions. They introduce variability into the relationship and thesis statement by influencing the strength or direction of the relationship across different levels or conditions of the moderating variable.
The research paper we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources

Relationship With The Independent And Dependent Variables
Mediating variables intervene between the independent and dependent variables, mediating or transmitting the effect of the independent variable to the dependent variable. They provide a deeper understanding of the causal mechanisms underlying the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Moderating variables interact with the independent and dependent variables, influencing the nature of their relationship under different conditions. They do not intervene in the relationship itself but instead modify or qualify the relationship based on different levels or conditions of the moderating variable.
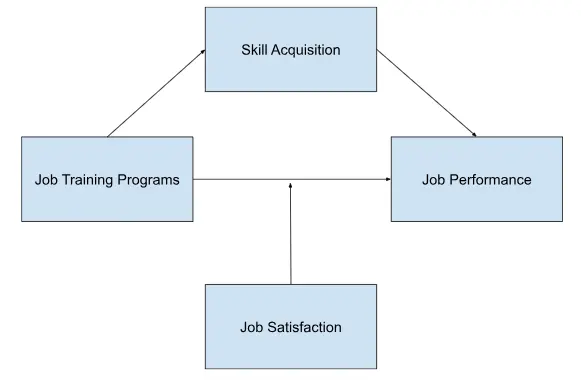
Consider a study examining the relationship between job training programs (independent variable) and job performance (dependent variable), with skill acquisition as a potential mediator. In this scenario, skill acquisition mediates the relationship between job training programs and job performance by explaining how the acquisition of new skills enhances job performance.
Now, imagine the same study but with job satisfaction as a potential moderator. Here, job satisfaction may moderate the relationship between job training programs and job performance by influencing the extent to which employees benefit from the training programs.
For instance, employees with high job satisfaction may exhibit a stronger positive relationship between training programs and performance compared to those with low job satisfaction.
| Feature | Mediator | Moderator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Explains the “how” of the relationship | Affects the “strength” or “direction” of the relationship |
| Impact on Relationship | Explains the process through which IV affects DV | Changes the interaction between IV and DV |
| Causal Relationship | Causally influenced by IV and influences DV | Not causally related to IV |
| Example | Exercise -> Sleep -> Academic Performance | Exercise -> Academic Performance (modified by Enjoyment of Exercise) |
Frequently Asked Questions
Mediating variables explain the mechanism or process through which an independent variable affects a dependent variable, while moderating variables influence the strength or direction of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables under different conditions.
In a study on the relationship between exercise (independent variable) and mental health (dependent variable), self-esteem serves as a mediating variable, explaining how exercise boosts confidence and reduces stress levels, thereby improving mental health outcomes.
In research on the impact of teaching methods (independent variable) on student performance (dependent variable), student engagement (moderating variable) may influence the strength of the relationship, with higher engagement enhancing the effectiveness of certain teaching methods.
Intervening variables, like mediating variables, explain the relationship between independent and dependent variables. Moderating variables, however, influence the strength or direction of this relationship under varying conditions, rather than explaining the mechanism itself.







