Abstract
This research aims to investigate internal communication strategies to keep employees motivated and engaged during COVID-19. The pandemic caused due to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has affected businesses worldwide, forced the offices to enter into downsizing and functioning with employees. The norms of social distancing have compelled many workers to work from home and increased their fears of losing jobs due to the uncertainties of the market and the suspension of revenue generation. DXG (a case company chosen for the study) has suffered from decreased staff motivation due to the COVID-19 pandemic as people are working from home and suffering from loneliness and distractions. The main aim of the study was to investigate the internal communication strategies used by leaders and managers to keep employees motivated and engaged during the COVID-19 pandemic along with the possibilities of making improvements. [NS1] To conduct this study a case company DXG has been chosen so that the strategies used and their impacts on perceived employee motivations can be assessed. The data collection in the study has been conducted to analyse the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the perception of job security and health concerns of employees along with the internal communication strategies that help improving employee motivation and engagement. The research has also investigated how the employees can be motivated and engaged with internal communication strategies during COVID-19.
A survey was conducted amongst 300 employees of DXG along with in-depth interviews amongst 3 senior employees of DXG. From the survey, it is found that the pandemic has impacted the job security perceptions of the employees whereas they use digital tools for communicating with their team members. [NS2]
Based on the findings from the interviews it was found that due to the pandemic, there have been performance delays due to communication changes within the company. This has reduced productivity in the firm and resulted in lay-offs, as there are not enough positions in the firm that can be accomplished by working from home. From the evaluations of the interviews, it was also found that using internal communication tools like Slack and others took employees a few days to learn and be acquainted with. Similarly, video conferencing was also not easy with additional obstacles such as their kids playing around or the shyness from coming in front of the screen or even issues of internet connectivity. Based on these findings the researcher formulates recommendations for the leaders and managers of DXG to improve the engagement and motivations of employees during the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic, internal communication strategies, employee motivations, employee engagement
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background
The coronavirus pandemic has impacted businesses globally as it has disrupted entire business operations and forced organisations to operate with a limited number of employees for maintaining social distancing in the office space (BBC, 2020). The uncertainties due to the pandemic have increased for the employees working in companies as there have been widespread lay-offs from jobs across industries throughout the world in addition to the creation of a situation in which the workers are forced to take pay-cuts. The topic of the research is to investigate the internal communication strategies to keep employees motivated and engaged during COVID-19. The case of DXG has been undertaken for evaluating the research topic as the staff of the company had been subjected to work from home (WFH) guidelines. There were also reports of low motivation and engagement of the staff against which the company has taken some steps for improvement. However, there remains significant room for improvement in the areas of increasing staff engagement and motivation by implementing effective internal strategies of communication.
Internal communication has a vital role in the organisation in terms of employee motivation and engagement. Internal communication is highly significant as it helps employees to align themselves with the business objectives, working processes and protocols of the organisation. International communication strategy is an essential practice of the organisation that needs to be developed and maintained within the organisation for getting proper employee performance and business success. Employees are the vital component of the organisation, where the performance and effort of the employees assist the organisation to gain expected business outcomes (Bieńkowska, Tworek, & Zabłocka-Kluczka, 2020). Internal communication strategies are developed for enabling proper communication and information sharing among the employees. Internal communication strategies also play a critical role in the development of the workplace culture as management develops an organisational culture in such a way that all internal employees can communicate with each other quite effectively (Alfalih, 2020). These communication strategies include the use of different technologies for remote communication and arranging meetings, brainstorming sessions, etc. so internal communication and collaboration among the employees can be maintained.
Employee motivation refers to the energy, commitment and creativity level of the employees to fulfil the regular job demand (Albrecht et al., 2015). The management of the company generally addresses both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation for involving the executives more in the work, which is beneficial from a business perspective[WZ1] . However, the rise of the pandemic and changed social structure has affected the regular business work process and thus the employee motivation. Most companies mainly focus on maintaining their constant profit generation, which has resulted in less motivation among the employees and the loss of thousands of jobs across the globe (Alfalih, 2020). [WZ2] Therefore, the role of internal communication strategies has become more significant especially during this pandemic.
Employee engagement is the process of involving the staff in the organizational activities and decisions to create a sense of ownership in them through a shared vision. Employee engagement displays the passion of the employees towards working for the organizational cause and deliver directed efforts for completion of the tasks (Quirke 2017). [WZ3]
1.2 Company overview
DXG or Digital Experience Group is a division of Wolters Kluwer and is one of the leading organisations that focuses on offering state of the art digital solutions to different business across the globe. The parent organisation employs a workforce of 18,000 and has its headquarters in the Netherlands from where it manages the worldwide operations. The organisation had been founded in 1987 and generated a revenue of €4.3 billion in 2018. DXG has concentrated on the adoption of contemporary technologies and innovation to offer digital products (Wolters Kluwer, 2020). The company remains functional as an internal component in Wolters Kluwer for formulating expert solutions for the business with the use of latest technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Natural Language Processing and Cognitive Insights for four large segments like Legal, Health, Risk & Compliance and Tax & Accounting.
1.3 Problem description
The pandemic caused due to coronavirus has altered the world economy largely due to the rapid closure of businesses and halting public interactions (BBC, 2020). This is due to the lockdown implemented by the government for reducing social contact and maintaining a physical distance. The rapid changes in the business environment and the global dynamics along with work from home for the employees have resulted in lower motivation and lack of engagement in addition to negative perceptions regarding job security and health concerns. Internal communication strategies of companies present an account of the overall plan of communication with the organisational employees and involve planning for the activities to be accomplished by the workforce for achieving the goals (Christina, Dainty, Daniels, & Waterson, 2014). Consistent internal communications ensure that their employees remain engaged and are motivated to perform consistently.
Employees and executives are the essential components of the organisational business. Business operations for the organisation need to rely more on the executives and their effectiveness (Ma & Zhan, 2016). DXG works on delivering corporate services and the development of digital solutions for clients with the use of advanced technologies and innovation. However, the company needs proper collaboration among the workers and needs to have an engaged and motivated workforce for coming up with unique solutions for the problems faced by the clients. COVID-19 has affected the entire business processes completely due to most of the employees working from home and thus improper management and lack of internal communication. [WZ4] COVID-19 has created the problem of uncertainties and negative perceptions in the employees across the corporations resulting in a lack of engagement and motivation as they have become increasingly concerned about their health and job security. As the virus is contagious, people including the organisational staff are required to undertake precautions regarding wearing masks outdoors and sanitising themselves in addition to maintaining social distancing. This has created health concerns and fear in the employees that have reduced their motivation to work whereas there are also concerns regarding job security.
COVID-19 pandemic has a large impact on employee motivation and engagement. Employees do not prefer to devote themselves to a working situation where safety issues are a major concern. An organisation like DXG prefers remote work and communication of employees, as internal communication needs to be established over the virtual platform so that the workflow remains unaffected. Many challenges occur due to the lack of internal communication strategies as improper communication and collaboration can lead to low performances and productivity among the employees. Management has to play a major role to work proactively to overcome this problem (Caligiuri, De Cieri, Minbaeva, Verbeke, & Zimmermann, 2020). Work from home scenario offers a level of solutions as the employees do not have to travel to their office during this pandemic as they have the luxury to work from the comfort of their homes. However, working from home provides a safe condition for the employees during the pandemic that can be a factor of motivation and engagement if proper internal communication is done. A good Internal communication strategy has the potential to engage the staff with common goals and keep them motivated despite such adverse conditions due to the pandemic.
1.4 Research aim and objectives
To investigate the internal communication strategies to keep employees motivated and engaged during COVID-19.
The research objectives of the study are as follows.
- To determine the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the perception of job security and health concerns of employees.
- To evaluate the internal communication strategies for improving employee motivation and engagement.
- To investigate how the employees can be motivated and engaged with internal communication strategies during COVID-19.
1.5 Research questions
The main research question for the study is as follows;
What are the internal communication strategies that can be implemented to keep employees motivated and engaged during COVID-19?
1.5.1 Sub Questions
The sub-questions for the study are as follows;
- What are the job security and health-related concerns of the employees due to COVID-19 and what is its effect on motivation and engagement?
- What is the present internal communication strategy practiced in DXG?
- How does the internal communication strategy [WZ5] help in motivating and engaging the staff during the COVID-19 pandemic situation?
Chapter 2: Literature review
The literature review chapter, first, evaluates the current state of knowledge about the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on employee perceptions regarding job security and safety. Second, it discusses the strategies of internal communication that are known for improving employee motivation and engagement along with their importance. This chapter also elaborates on how organisational staff can be motivated and engaged during unprecedented times like COVID-19 with internal communication strategies.
2.1 Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the perception of job security and health concerns of the employees
As explained by Chumg, Seaton, Cooke, and Ding (2016), assessment of employee perception helps to determine the level of satisfaction of the workers in the organisation in addition to their morale. The perception of the employees about their work in addition to their morale is the determining factor for satisfaction and chances of leaving the company. On the contrary, ROLLINSON, (2008) argued that the perceptions of the employees are generally affected due to the conditions at the workplace in addition to the culture, management and interpersonal relationships. The perceptions of the employees can be understood by conducting surveys across the firms that help the management to take decisions regarding HRM strategies in addition to shaping the appraisals.
As per the findings of Bartsch (2020), COVID-19 has changed the lives of people across the globe by bringing major changes in physical socialising and travelling. The onset of the pandemic has caused the world to shift its pattern and thus eventually affected every single aspect associated with this pattern as thousands of people across the globe have died due to the virus and millions have been affected. An article published in the (BBC, 2020) explained that due to the forced lockdown across the globe, economies have plummeted to a new low as almost all the sectors have been forced to shut down their operations. This has led to massive job losses and salary deductions that have increased the stress among employees and negatively? impacted their perceptions. The loss of business in the pandemic has resulted in declining to negligible revenues for many companies across the world thereby forcing them to send the employees to mandatory leaves without payment in addition to deducting up to 50% of wages for the existing staff (Dey, Frazis, Loewenstein, & Sun, 2020). Such circumstances have severely impacted the sense of security of the employees regarding their employment as there are instances of layoffs in many companies. This affects the ability to work for the employees as they remain uncertain regarding their future in the workplace and the flow of safe income.
Based on the perspective of Alfalih (2020), the global concerns regarding maintaining safety by wearing masks for social and public outings in addition to the use of hand sanitisers and washing hands periodically have also created a sense of pressure among the employees. This is because they are required to battle the dual aspects of maintaining their professional job and ensuring earning their livelihood in addition to maintaining the safety and wellbeing of their family. Jasmine (2019) contradicted[WZ6] this by saying that the perceptions of the employees are affected due to the dual concern that leads to mounting pressure in them thereby affecting their quality of life in addition to the performance at work. Additionally, the lack of physical meetings at the workplace and working in the office environment has resulted in the lack of motivation and sense of accomplishment among the staff as they are forced to work from home in addition to managing the household work. Despite the situation of a pandemic, the work pressure and stress remain the same and have even increased in some situations due to the complexity in addition to the mounting pressure from the management to deliver effective results. On the other hand, as employees have started working from their homes, most workers have turned digital in this plight (Sembiring, Fatihudin, Mochklas, & Holisin, 2020). The majority of the workers were not accustomed to this concept but tried their best in getting accustomed to it. This has added more pressure to their performances and eventually influenced their motivation level towards their works.
As explained by Mullins (2016), the perceptions of the employees influence organisational productivity depending on the attitudes and efficiency. Negative employee perception due to the Covid-19 pandemic is caused by the salary cuts, forced leaves and loss of employment (BBC, 2020). The sudden and unplanned lockdown across the megacities has resulted in losses for the business and the stoppage of all kinds of operations. The restricted consumer spending on items apart from essential goods has resulted in the creation of deep uncertainty in the minds of the employees as the organisational profits have dwindled causing massive downsizing across industries (BBC, 2020). This has resulted in the organisational behaviour of the companies to be uncertain and unfocused.
Forsythe, et al., (2020) explained that perception is the cumulative procedure of interpretation and organisation of the sensory impressions by the individuals that can generate meaning based on the present environment. It has been found after the survey that working from home needs to be portrayed in a proper way where the employees should be motivated and aspirations should be given to them as their personality development skills need to be inculcated to have a better working environment (Blundell, Costa Dias, Joyce, & Xu, 2020). According to Caligiuri, et al., (2020), unnatural situations like the pandemic have caused working from home to become a norm that is not enjoyed by the employees as it has become a compulsion that disrupts the working environment thereby affecting the perception of job security of the employees.
The pandemic has disrupted the normal work habits of the staff, as they are required to operate from home or visit offices in fewer numbers (Bieńkowska, Tworek, & Zabłocka-Kluczka, 2020). However, there is a concern among the workforce that they might be called back to the office and required to work at the office buildings that might put them at a safety risk and increase the probability of contaminating the virus (Shankar, 2020). As explained by Christina, et al. (2014), organisational behaviour is the overall understanding and estimation of human behaviour in the organisations at the individual and group levels. He added that organisational behaviour incorporates the perceptions of employees in various situations and it is important for maintaining the interpersonal relationship among employees and maintaining effective communication. As per Chumg, et al. (2016), organisational behaviour is a product of the motivational level of the employees along with their perceptions of different situations. He added that the perception of employees is essential for understanding the activities and tasks to be performed for contributing to the overall organisational goals along with understanding their importance.
As explained by Shankar (2020), the analysis of perceptions of the employees enables the organisational managers to determine the behaviour of the staff for completing their respective tasks along with clarifying their roles. HUCZYNSKI & BUCHANAN (2013) contradicted that, the perception of the employees influence their levels of motivation and the ability to perform at the individual level [WZ7] only?. The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in creating a negative perception among the employees that affect their work performance along with the ability to communicate by working from remote locations. This also results in the degradation in the quality of decision making as groups and more conflicts at the organisational level due to increasing stress levels. The companies are required to ensure that they incorporate the theories of personality while managing organisational behaviour to shape the perception of the employees positively. The attribution theory is relevant for companies to manage employee perceptions as they judge the circumstances differently. This is based on what is attributed to them considering the behaviour (Shankar 2020). [WZ8]
Mullins (2016) states that Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic theory states that the belief of individuals is motivated by the unforeseen and unpredictable circumstances in comparison to logical and conscious thoughts. The theory incorporates the perspectives of Id along with the ego and superego of individuals. The Id denotes the innermost component of the personality of an individual that requires immediate satisfaction whereas the ego enables people in managing and dealing with the external world with rational thinking (ROLLINSON, 2008). The superego is an unconscious component of the workers that incorporates the traditional values. The Id component of the theory is relatable to employee perception during the pandemic as they are required to be provided reassurance about their job safety whereas the ego component can be met by presenting a plan of action at the organisational level. The superego part enables the employees to deal with the situation by accepting pay cuts and wait for the industry to experience growth.
2.2 Internal communication strategies for improving employee motivation and engagement
2.2.1 Employee Motivation
As explained by Menges, Tussing, Wihler, & Grant (2017), employee motivation is classified into two categories like intrinsic and extrinsic which assist the management to make the employees proficient with the work process of the company. However, Meske, Kissmer, & Stieglitz, (2018) said that compensation, promotion and performance-based payment or incentive are included under extrinsic motivation whereas intrinsic motivation comprises regular communication, recognition and appraisal. The formation of groups over the digital medium would enable the companies to be incorporated with all of the colleagues.
As suggested by Gould-Williams (2016), motivation is defined as the internal desire and driving force that influences the intensity and direction of behaviour. Motivation is essential for the employees in an organisation as it enables them to have a proper direction to focus their efforts and guides them towards providing the right intensity in addition to encouraging them to deliver persistent efforts. The employees who are motivated in an organisation deliver better quality performance and have greater productivity compared to those who are not (Bachman, Norman, Hopkins, & Brookover, 2016). Establishing motivation among the workforce enables the organisation to achieve the behaviour dimension of recruiting and retaining the workforce along with establishing dependability in the employees to perform tasks along with ensuring creativity and innovation at the workplace.
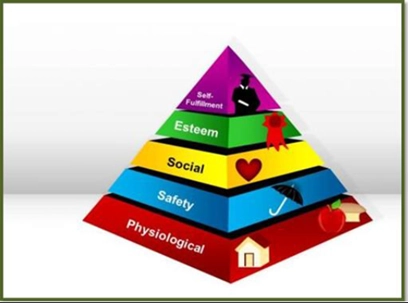

Figure 1: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Source: Bachman, Norman, Hopkins, & Brookover (2016)
As explained by Bachman, Norman, Hopkins, and Brookover (2016), Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory groups the five needs of employees depicted through gFigure 2: Conceptual framework.
rowth and deficiency needs. The physiological needs are the basic needs of the employees and it creates a feeling of clarity, control and appreciation whereas the safety needs of the employees include the delivery of consistent monetary remuneration and job security (Gould-Williams, 2016). The social needs of the employees are fulfilled through the establishment of consistent communication and engagement across the workforce whereas the esteem needs are fulfilled by providing constant feedback. The self-actualisation needs of the employees are fulfilled by providing training and recognition for good efforts as a means of enabling the workers to reach their full potential. Continuous motivation and engagement of the staff are essential during the times of COVID-19 to make them feel relevant to the organisational goals and enhance their confidence levels to perform.
As explained by Liu and Yuan, (2015), communication has always been one of the best tools that enhance the working of all the employees in a company in a better and structured way. Communication helps a company to convey its plans and the rules the company follows. Internal communication helps to inspire and motivate the employees very much. It is a process that undergoes constant rethinking. Internal communication helps in inspiring the local leaders and the communicators easily. The effective approach to internal communication highlights the location-specific needs (Venkatesh, 2020). Employees of organisations are highly comfortable when discussing the local topics and this provides an insight into the culture, strategy and engagement of the local ideas in the company. Thus, it can initiate comfort in the working scenario of the company.
2.2.2 Employee Engagement
As explained by Albrecht, Bakker, Gruman, Macey, and Saks (2015), employee engagement is defined as the process of establishing a sense of passion in the employees about their work and the delivery of discretionary effort at the workplace. Employee engagement provides an understanding of the interrelationship among the organisation and its employees that can be achieved by establishing a culture of employee development along with focusing on transparency and empowerment. Employee engagement is essential as it enables the companies to retain skilled and experienced staff for a longer time along with increasing the levels of productivity (Ewing, Men, & O’Neil, 2019). Workplace engagement induces a sense of satisfaction in the employees as they work for a higher purpose rather than earning remuneration as they dedicate their efforts to the overall betterment of the organisation. Communication is an integral component of establishing employee engagement as it facilitates the development of strong working relationships between the workers that subsequently increases the rates of productivity (Quirke 2017). Clear and consistent communication at the organisational level helps to build trust among the workers and keep them engaged.
2.2.3 Internal communication
As suggested by Campos, et al., (2018), the conversation of the team leader with the employees face to face is an example of internal communication that initiates and boosts the confidence of the employees to a great extent. In the era of video conferencing leaders can easily communicate with their employees while working in the different geographical locations. But in a survey, it has been found that the in-person meetings clear the potential misunderstanding as it increases empathy, understanding, and even reduces the chances of the miscommunication easily (Ozkeser, 2019). The leaders involve themselves to receive the employees’ feedbacks personally and this process imparts a positive effect on the employees. Constant internal communication is needed by the leaders and managers across organisations to reassure the employees about the fulfilment of their safety needs and physiological needs in the form of timely remuneration and job security in addition to opportunities for learning, growth and recognition.
2.3 Employee motivation and engagement with internal communication strategies during COVID-19
As explained by Garcia-Carbonell, et al., (2016), internal communication strategies in companies help in the transmission of information internally within an enterprise with the employees regarding the business goals. They added that this involves planning down the activities for reaching out to the goals. The internal communication is based on the information-sharing regarding business processes in addition to playing a crucial role in motivating the employees for performing their assigned job roles and maintenance responsibilities with higher accountability. Internal communication strategies for the business organisation are also being used as the platform through which the organisation aim towards building a relationship with all the organisation members so that better ideas and thoughts can be generated and implemented within the organisation (Murphy, 2017). Internal communication strategies in DXG involve communication through the leaders using a top-down approach as the information is passed from the subordinate managers to the employees.
As explained by Goodman (2019), internal communication in firms pertains to the changes that are to take place in addition to crisis communication like a disruption in business due to COVID-19. In DXG, the internal communication strategy using digital tools like Google Hangouts, Zoom and internal cloud server helps to establish seamless internal communication with the employees during COVID-19 to discuss emergence response plans (Wolterskluwer, 2020). Based on the opinion of Quaratino & Mazzei, (2018), using internal communication strategies facilitates peer communication to improve employee engagement and fulfil some of the motivational needs[WZ9] . He added that the establishment of a two-way communication or a bottom-up communication is beneficial for taking employee feedback and motivating them through inclusion in decision making. Besides, the internal communication system also offers flexibility to the employees so that they can arrange the information, prioritise the activities and then perform them which increases the chances of making the business successful. Consistent internal communication with the employees is needed to ensure that they are aligned with the organisational motives and have a positive perception of their position in the organisation. Providing an added sense of security to the employees can add to their performance and motivation at work that would compel them to display exceptional performance at work.
As explained by Neto, et al., (2018), internal communications in organisations can facilitate the creation of resilience and encourage the staff to collaborate and enhance the overall productivity. Ciobotă (2017) added that a situation like COVID-19 is unprecedented and disrupts the business operations due to forcing the companies to work with a limited workforce and take forced leaves. Internal communication and engagement help to provide a feeling similar to being in the office to the employees to help them feel comfortable to work from home. Firms can motivate their employees using internal communication tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams and Google Hangouts. Besides, using the internal communication strategy as the one platform has also managed the organisation in maintaining documents along with keeping records that make it possible for the employees to perform their tasks with integrity.
The situation of COVID-19 has made it difficult for the organisations to make decisions and letting the employees know about them. Therefore, the implementation of an internal communication system through a virtual platform makes it easier for the organisation to motivate the team by inspiring them towards accomplishing the objectives of the organisation. As explained by Ewing, Men, & O’Neil (2019), the internal communication platform also encourages the employee’s input forwarding their ideas and thought processes through which informed decisions can be undertaken and better organisational success can be achieved. One of the positive factors that the internal communication platform brings is feedback that assists the organisation in undertaking decisions and eliminate challenges that increase risk. Therefore, building internal communication strategies during the unprecedented situation such as COVID-19 plays a vital part in motivating employees and maintaining higher work operations of the business enterprises.
The Digital Experience Group (DXG) at Wolters Kluwer has delivered consistent efforts to enhance the profitability and revenue generation of the company with the help of digital solutions (Wolters Kluwer, 2020). However, the pandemic has resulted in the loss of collaboration among the workforce due to dispersal from the workplace and working from home. This has disturbed the consistent communication and internal regulation in the company and negatively affected employee motivation and engagement due to perceptions about job security and safety. However, with digital tools and instant messaging applications, it would be possible to keep the employees engaged during the pandemic caused due to COVID-19. Additionally, this can help to create the base for the workers to remain connected with the parent firm and receive updates about all the events in the company. The firm would be able to establish a sense of trust among the workforce that has led to a greater experience of the staff and combat the unprecedented times with ease. Maintaining relationships with the employees and maintaining interactive communication is essential for keeping them motivated and influencing their perceptions to become more positive in addition to providing a sense of security. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory, when applied in this organizational context, can help to establish a sense of control and security among the staff thereby improving their motivation and engagement with internal communications and support. [WZ10]
2.4 Research gap
There is a gap in the literature regarding the determination of the internal communication strategies used by the companies as the crisis of the COVID-19 and its impact on business seems unprecedented. There is not much research yet, since the issue only arose at the start of 2020. It is affecting many companies worldwide and research is needed to investigate and test internal communication strategies in this new situation.
2.5 Conceptual framework
Based on the current literature findings and the research gap the following conceptual framework has been developed. The conceptual framework shows that as a result of the pandemic situation the leaders and managers of the case company DXG adopted a new workplace environment that is work from home and as a result, there was a change in the communication method used before. The conceptual framework represents the interrelationships among the elements of the research. New internal communication strategies, as well as challenges of working from home like giving time to family and children or working from a new environment as well as poor internet connectivity and others, are the independent variable of the study whereas employee motivation and engagement along with COVID-19 are the dependent variables. The internal communication strategies in an organisation ensure collaboration between the workforce and accurate transmission of information whereas the motivated and engaged employees deliver better performance and easier to be retained. Therefore, it may be stated that consistent internal communications and leadership abilities lead to enhance motivation and engagement of the staff that is crucial for influencing their perceptions positively during COVID-19.
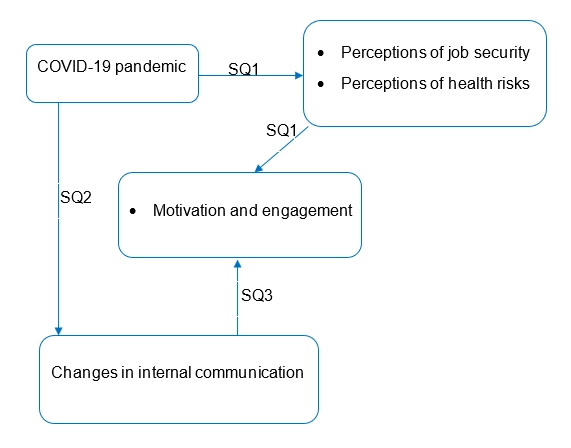

Figure 2: Conceptual framework.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
3.1 Methodology
The research methodology is based on a mixed-method whereby both qualitative and quantitative research methods have been used. Quantitative methodology is based on the objective measurements of the data collected about the study variables using survey methods. Also, qualitative research has been done using interview methods. The methods facilitated the researcher to understand the perceptions of the employees of DXG regarding their levels of engagement and motivation during the pandemic while working from home. The impact of new internal communication strategies on the motivations and engagement of employees was also evaluated. The quantitative methodology has been undertaken to conduct the study systematically with the survey whereas the qualitative method has facilitated with the interview for identifying the internal communication strategies used in the organization (Saunders, 2011). The research methodology has been presented in a structured manner in the following sections.
The quantitative approach in the mixed methods considers the numbers and calculations for analysing the relationship between numerally measured variables like employee motivation and job satisfaction along with internal communication strategies. This is done with the application of statistical techniques (Mellinger & Hanson, 2016). Surveys are used for collecting the quantitative data with the help of distributing the questionnaires containing close-ended questions over online platforms like emails and Facebook.
As for the qualitative approach, an interview was conducted with the organisational managers to address the sub-questions 2 and 3 and find all the internal communication changes made as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic situation and the impact of these changes on the motivations and engagement of the employees of DXG. So, by using in-depth interviews for qualitative assessments, the aspects of motivation and engagement of the employees along with the internal communication strategies that are used in the company DXG.
3.2 Operationalisation for the survey
The operationalisation of the research has been based on the establishment of a link among the various variables identified in the conceptual framework (Williams, 2011). In the case of a survey, sub-questions 1 and 2 have been mainly focused on whereby the impact of structural changes in business on employee perceptions and the existence of internal communications were explored. For this survey, the key concepts that can be used for the current survey method are job securities, health concerns, job satisfaction, employee engagements and types of internal communications. Based on the literature review, job securities are concerns that employees have in case of a crisis where the employees have the risk of losing their job and remain unemployed. In the case of the COVID-19 pandemic, it was found that many companies globally were laying off employees for financial survivability. Similar, the infection rate from the virus was so high and dangerous, the employees and people globally had to remain at their homes and either study or work from home. This also increased their concerns of health. The next concept that comes to addressing is employee motivation, which means the perceptions and attitude of the employee towards its employer and their workplace responsibilities. The fourth concept is engagement, whereby, the rate or intensity of the work the employees had to do during the pandemic situation was also defined by the workplace environment they were working in. The last concept in this segment is the application of internal communication tools as the strategy to address all the previous four concepts. Therefore, the study conducted a survey that comprised of ordinal measures to explore the perceptions of the employees of DXG on these concepts. The variables in the research were described by using proper instruments during the research design. COVID-19 has been operationalised through the expression of the determination of its impact on health concerns and job security perceptions of the organisational staff whereas the internal communications strategy had been operationalised in terms of being effective in engaging and motivating the workers. Engagement and motivation of the staff as variables have been operationalised by analysing its impact on organisational productivity and performance.
3.3 Operationalisation for the interview
For the interview study design, the researcher used open-ended questionnaires that asked different questions on how the pandemic affected the business communications and if any new tool or strategy was adopted. Also, the interview enquired how the pandemic situation as well as the changes in the organisation may have affected the employee motivations. Furthermore, in-depth questions were also asked for the types of internal communication strategies used due to the changes in business structure and their impact on the employees. Again, in this segment two sub-questions were addressed using the primary qualitative interviews and they were 2nd and the 3rd sub-questions. To conduct the operationalization for interviews, the interview was used to gather in-depth information about the present internal communications carried in the business and how it can help the employees to cope with the new changes. The main concepts that will be investigated using the qualitative interviews were internal communication strategy, the motivation of employees and engagement of employees. Internal communication strategy is the channel that managers and employees and the board members of the company use to communicate with everyone in the company or to pass on information to others. For example, to make an announcement, the manager may send emails to all its their team members and this internal communication. It was further found from the literature review that the better the communication between the employees and the managers, the more is the level of bonding between the two and also increases the motivation of employees to work effectively. Similarly, communication is also the component that holds the level of engagement amongst the employees. However, due to the current pandemic situation, the communication systems have changed and it is, therefore, important to explore the communication systems used by the managers and employees while the employees were working from home and the level of engagement the employees have due to the current scenario of the pandemic situation. The findings from the qualitative assessments or interviews have been presented using thematic analysis. The transcripts from 3 managers and senior executives of DXG were first recorded and then transcribed to form the interview transcripts and once the transcripts were made, codes and important sentences were highlighted by repeatedly examining the 3 transcripts and then segregating them to form themes and sub-themes. Eventually, the current thematic analysis resulted in 4 main themes with no sub-themes. In the interviews, 2 senior executives and 1 manager from DXG were included post their permission through verbal confirmation for telephonic interviews. Both the senior executives were from the project management department and the manager was from the IT department. The exact designation of the participants has been kept confidential as per ethical considerations. All the participants were male and between the ages of 30 to 37 years.
3.4 Sampling strategy
Undertaking a sampling strategy within the research study facilitated the researcher in saving extra research costs.
Sample Survey
Besides, the results that have been drawn out of the survey process can also be evaluated accurately that generates conclusive research findings (Snyder, 2019). [WZ11] The evidence gathered also signifies that sampling within the research makes it easier for the investigator to process the information more efficiently and successfully to perform the study. Simple random sampling has been considered by the researcher to provide equal opportunities to all of the employees of DXG to get selected in the survey process. Besides, simple random sampling also removes biases from the selection procedure. Simple random sampling is also appropriate for the research as it benefits the researcher in making the research findings generalised and free from biases (Taherdoost, 2017). The target population that had been undertaken during the study is 1350, where the confidence level of 95% and 5% of margin of error have also been undertaken while considering the sample size. Therefore, the calculated sample size for the study is 300 respondents. Random sampling is being considered while performing a quantitative survey method as it helps the researcher in laying down structured data collection instruments. The findings that are being gathered from the quantitative survey method are also being easier to present, summarise and generalise (Kelley-Quon, 2018). The quantitative data is being mainly collected from the employees of DXG upon whom surveys in the form of questionnaires will be performed. The questionnaire will be distributed through email and the responses will also be gathered from the same procedure. The target population for the survey was 1350 employees of DXG.
Sample interview
The interviews targeted the senior management employees and managers of DXG. As for the interviews, a purposive sampling plan was used whereby the close associates of the company to the researcher were targeted for participating in the interview. These subjects had more than 5 years’ experience at the company and were well qualified to answer the questions on behalf of the organisation. Initially, 6 senior employees and managers were targeted and they have been approached before the festive period of Christmas, but only 3 managers gave permission and had time for the interviews. Purposive sampling had been done to increase the chances of gathering insightful knowledge about the areas of deficiency in the present internal communication strategy at DXG and deriving areas of improvement. The sampling was done for representing the managers having a good experience and domain knowledge in the company. Each of the interviews was done via telephone and approximately each of the interviews took at least 30 to 40 minutes.
3.5 Limitations of the research design
There are limitations to using both quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. One limitation that was experienced during the conduction of the study was that the survey participants have a habit of leaving out questions if they do not answer or do not want to answer the questions, and this raises data gaps and affects the process of statistical assessments (Kumar, 2019). The study found at least 5 to 6 responses [WZ12] after submission of the questionnaire and so had to reject its inclusion. Another limitation of using interviews using telephonic methods is that there are multiple disconnections and as a result, the interview process cannot be conducted in one flow and this also reduces the time for conducting the interviews (Kumar, 2019). This happened in the case of interviewing one of the senior executives whereby there were multiple disconnections due to poor weather or other reason and this affected the data collection process. The fact that only 3 managers were able to be part of the interview is a key limitation of this study. Furthermore, another limitation is that on the telephonic interview the non-verbal communication is not possible to be seen by the researcher and the intentions of the interviewee cannot be known.
3.6 Analysis
The analysis of the collected information will be done through excel where charts and graphs will be constructed to interpret results. Besides, statistical tools will also be used in terms of analysing quantitative data information. Furthermore, to find an in-depth assessment of the changes to the organisational structure and business communications as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, a qualitative analysis was also done using an interview study design.
Chapter 4: Results
4.1 Demographics and General description
Gender
Based on descriptive assessment, it was found that 57% of the participants were male employees and 43% of the employees in the survey were female. Therefore, it may be implicated that only 57% of the total male and 43% of the total female employees currently employed in DXG have interest and concerns about job security and health as a result of the pandemic situation.
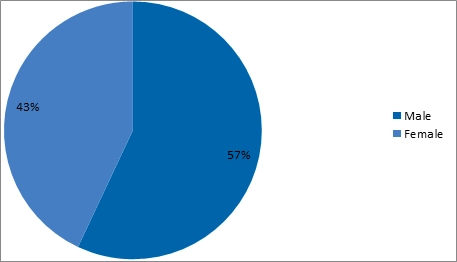

Figure 3: Frequency distribution of Gender
Age
It has been also found that the survey participants are mainly from the age group of 25 to 44 years (47%) followed by 36% were from less than 25 years and only 16% were from the age group more than 44 years. These employees that participated in the survey and are worried about job security and health due to pandemic situation have a range of age between 22 to 57 years. Moreover they are concerned with plus its effect on motivation and engagement due to changes in the current business structures.
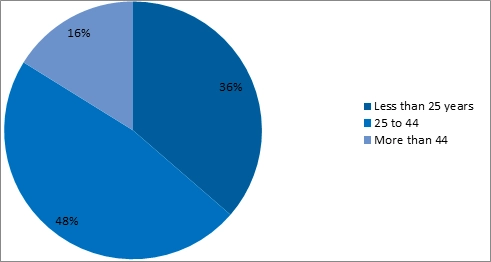

Figure 4: Frequency distribution of Age
Years of experience
Furthermore, over 60% have an overall work experience of 5 to 10 years followed by 24% with less than 5 years of experience and only 9% have work experience of more than 10 years and this is also supportive from the survey findings that about 16% of them are aged more than 44 years. It also implicated that the majority of the employees that are concerned about the effect on motivation and engagement from working at home or other changes in the business structure have varied numbers of experiences and comprises of both freshers and veterans who may have equal threats to job security.
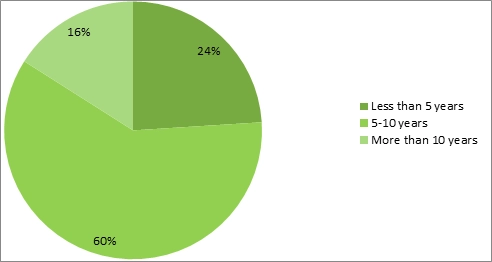

Figure 5: Frequency distribution of Years of experience
Educational qualification
As for the educational qualification of the participants or employees of the case company it was found that 66% of them have a graduate or postgraduate degree and 22% of them have an only diploma or certificate degree or including graduation and only 11% of them were PhDs which means they may be senior executives and managerial level employees.
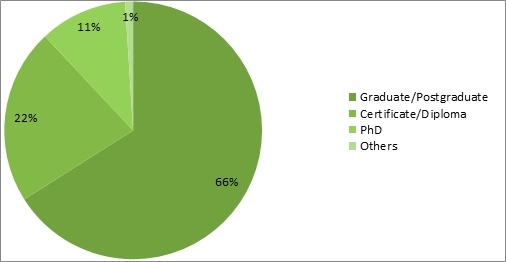

Figure 6: Frequency distribution of Educational qualification
Impact of COVID-19 on the job security perceptions
In this section, the perceptions and knowledge of organisational processes and communication systems used were explored and it was asked about the job security perceptions due to COVID-19. In this regard it was found that 73% of them accepted that they were worried due to COVID-19 because their colleagues and friends had lost jobs due to the economic impact from when COVID-19 had started. But only 1% of the employees denied the same either because they had recently joined and are [WZ13] not aware of the same. So, it may be stated that the majority of the employees that may have joined recently or working for a long time have threats of job security and therefore, may also affect their job motivations and engagement.
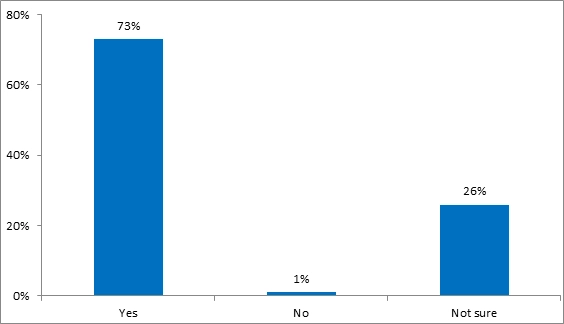

Figure 7: Frequency distribution of COVID-19 impacted your job security perceptions
COVID-19 concerned you with health impacts
Fig 8 is about if the employees perceived that COVID-19 concerned them with health impacts like infection and hospitalisation or even affecting their family and over 70% of them accepted the same. However, [WZ14] only 4% of the participants denied any health risks or impacts either because they are not aware of the mortality rate from COVID-19 and the danger to health if contracted to the virus. As mentioned before, it is clear that the majority of male and female employees from DXG have a strong feeling that they may get an infection and this may further impact their job engagements and others and may also harm his/her family members.
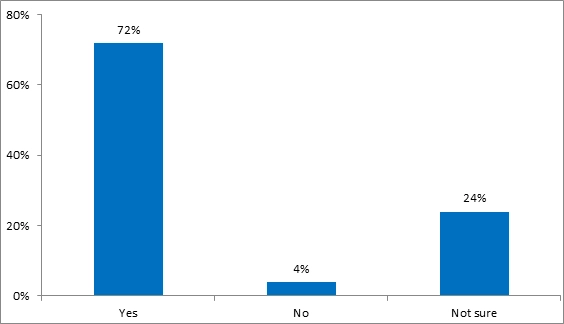

Figure 8: Frequency distribution of COVID-19 concerned you with health impacts
Did the company have internal communication systems before COVID-19
Fig 9 is about the presence of internal communication tools like E-mails, Google Hangouts and others for instant communications and information sharing and over 60% of them were found to accept that there were internal communication systems ways before COVID-19. However, there were 33% of the employees who have no idea if there were such communication systems before the COVID-19. Therefore, it is clear that the DXG has already been using some of the virtual communication tools and strategies as internal communication methods and so, must not harm their engagements or motivations expect that they will be working in a new environment.
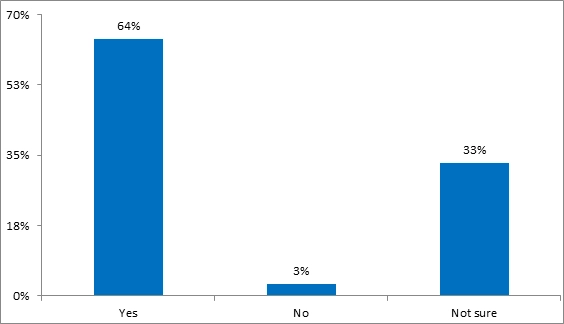

Figure 9: Frequency distribution of did the company have internal communication systems before COVID-19
During COVID-19 any new internal communication method was used
Furthermore, the employees were also asked if the company adopted any new communication tool after the COVID-19 pandemic and again 73% of them agreed to the same. This may indicate virtual workplaces and video conferencing tools may have been used for communication and information sharing. However, 24% of them have no idea either because the department they work for did not need communication tools or new communication tools after COVID-19. New communication methods are obviously[WZ15] needed as people will be working from home and they do not have tools installed in their home PCs or laptops and so a more common or easy tool for communication has to be adopted to improve motivations and engagement.
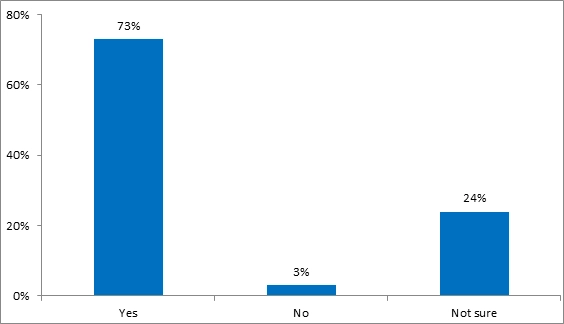

Figure 10: Frequency distribution of during COVID-19 any new internal communication method was used
Which of the following communication tools did you use?
In fig 11 different types of internal communication tools were reviewed for the most common tool to be used for communication after COVID-19 and virtual working and it was found that 55% of them have increased the use of E-mail tools like Outlook and Gmail and others. 26% of them use instant messaging tools like WhatsApp, Hangouts, Slacks and others for file sharing and casual communication with teams and leaders. Only 16% of them frequently used video conferencing systems for meeting and internal communications. Therefore, the present internal communication strategies are mostly virtual methods whereby information and files are sent within the company and sometimes, the managers may also use other methods like telephonic conversations or virtual voice calls that will suit the current situation.
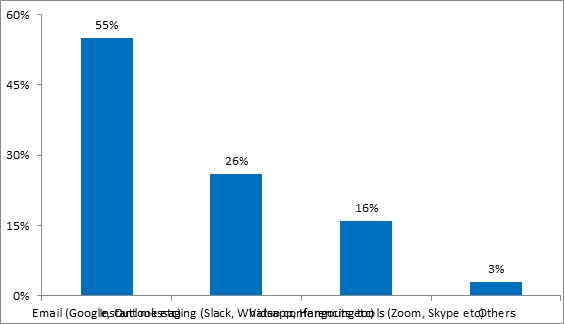

Figure 11: Frequency distribution of communication tools used
4.2 Interview results
4.2.1 Themes and codes
In the following tables 4 and 5, codes from the interview transcripts and themes have been presented. Four main themes were identified from codes and emerging themes developed and has have been described in the following sections. These themes and codes developed from the interview transcripts will be relevant for sub-questions for 2 and 3.
Table 1: Codes and emerging themes
| Codes | Emerging-themes | Main themes |
| financial and operational challenges, complexity in business operations, change of business environment, stopping of operations, uncertainty, supply chain impacted, work from home, different working hours, digital demand, loss of jobs, low workforce engagement | Impact of the pandemic on the company | Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the company infrastructure |
| both positive and negative, layoffs were negative, employees were efficient to complete tasks faster, employee communication was negative because of work from home, internet issues for employees, the flexible working environment was positive | Positive/ negative impact on the company | Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on employees |
| employee salary tensions, salary delayed so employees may be worried, some employees were delayed off so job security may be affected, poor employee motivations, virus infection-related worrisome, employee engagement was low at one point and so motivations may have decreased, employee trust affected, the gap between team leads and teams, employee engagement decreased, reduced communications affected motivations | Changes in business and impact on employees’ motivations | |
| moderately, fears of layoffs, fears of pay cut or no salary, challenges of working at homes with family and kids around, difficulty communicating with managers and teams, fear of infection and family health, disrupted the timing of work and other daily work, work-life imbalance, internet and telecommunication issues | The coping ability of the employees | |
| digital communication strategies used like Google Meet and Zoom, earlier the company did not allow to share files through WhatsApp now employees can adopt Slack, an internal communication tool that is both safe and cloud-based, e-mail already being used, Google Meet for video conferences, communication systems remain the same: teams report to team leads and team leads reports to managers and managers to head of departments and so on | Changes in communication strategies | Changes in the communication strategies as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic |
| positively, will need time to get acquitted with Slack and video conferencing methods, may face challenges of video conferencing, reduce the gap in communication, | Impact of changes in internal communication on employee motivations | Impact of new communication strategies on employees |
4.2.2 Theme 1: Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the company infrastructure
Interviewee 1 quoted that “change of business environment like people are now working from home, people talk over video conferencing, lack of tracking of employee performance, a company working virtually and dealing with customers and suppliers virtually are the major changes due to corona.” On the other hand, interviewee 3 stated that the main changes were “financial and operational challenges [which] increased and affected the entire business operations, the company was closed for a month or so, and then again we had to adopt digital and virtual methods of operation so that the ongoing projects can be completed.” The disruption due “COVID-19 pandemic is likely to lead to the permanent shut down of many businesses, but not DXG though, [as they are] unable to bear the financial losses and disruptions caused by the pandemic. To get over the current situation, DXG is trying to run offices and administration jobs through the ‘Work from Home’ mode. DXG trying to cope up with the economic turbulence caused due to the COVID-19 through the usage of disruptive technology by working from home concept.” Based on the implications of the interviewees, DXG had applied WFH work structure like any other company globally that were able to provide with Work from Home model for their employees to reduce risks of spreading the infection, health threats to employees and others. As a result of the pandemic, since DXG had adopted WFH options, it helps the company to keep the operations running. According to interviewee 1, “The WFH mode is helping DXG in keeping their operations going, in a limited way. Even though there are many positives and negatives aspects of work from the home concept as during this COVID-19 crisis, people working on WFH, are compelled to live in social isolation and emotional distancing. One can balance the responsibilities of work-life domains, especially when the life domain needs as much attention as to work, during these difficult times.”
4.2.3 Theme 2: Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on employees
Interviewee 2 quotes that, the “pandemic has both positive and negatives like we had to lay off some of the middle and low-level employees that were not immediately associated with any of the ongoing projects, and there were also gaps in communication which as a result may have caused some employees to rethink and ask if their jobs were safe.” Interviewee 1 also quoted that, “as a result of new work from home, many employees complained about poor internet affecting work performance, communication gaps with managers.” The coronavirus pandemic has “brought significant pain and hardship to workers for the company DXG. With redundancies and business closures, and widespread disruption even within ‘safe’ jobs, employees are having a difficult time including DXG.” Therefore, DXG has had to shift their work and workplaces affecting the very foundation of employment relations. As a result most of the employees working remotely lacked interactions with colleagues and this also affected the employment relations with managers and others. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic led work from home options especially for women, made it hard for work-family balance. With lack of schools and daycare due to covid-19, employees that were also parents were affected as they had to homeschool and even look after their children all the time. According to interviewee 3 “many parents are also working their paid jobs from home, while others have heightened financial concerns due to losing their job, and yet others involved in healthcare may be living away from their families to reduce exposing them to the virus also in case of DXG. Whatever the circumstance, the work-family balance has become increasingly challenging. Given the impact, the COVID-19 pandemic has had on employees’ work and professional lives and business priorities overall, talent management leaders are debating whether to adjust their performance review process this year.” Furthermore, challenges of communicating with leaders or a team because as mentioned before WFH employees may not be acquainted to the new task, or may be comfortable working at different hours and so affects the communication systems.
4.2.4 Theme 3: Changes in the communication strategies as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic
Interviewee 3 quoted in this regard that, “earlier the company did not allow sharing files through WhatsApp but now employees can share messages and can get replies instantly.” Similarly, interviewee 1 also quoted that they “adopted Slack, an internal communication tool that is both safe and cloud-based, e-mail already being used, Google Meet for video conferences, using Slack we can send updates and reports easily in a safe method and all files are stored in cloud even if the receiver is not able to retrieve information at the time, and we have used the premium version where we can send over millions of messages and files and store thousands of GBs of files secured.” As Cal Henderson the co-founder of Slack states, “Whether you’re using Slack already or are considering Slack to help you to manage remote work under the current circumstances, we want you to know that Slack has comprehensive plans in place to ensure that we remain up and running.” The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in the need for internal communication because of new working practices, work from home employees and working at different hours. Therefore, businesses like DXG adopted strategic communications to manage crises, conflicts and mitigate risks by specially focusing on internal communications. Internal communication is of ardent need in a time of the COVID-19 pandemic as it is hard for employees to work effectively and poor performance may affect the standards and performance of the company as a whole. Internal communications may involve developing the motivations and engagement of employees through effective internal communications development and training to positively impact employee performance and motivations. Interviewee 2 also stated that “digital channels such as enterprise social media, on-demand or live stream videos, and tele-conferencing used in employee communication and engagement, or examine relevant issues such as employee boundary management, role conflict, and innovation and creativity in the technology-mediated environment during the COVID-19 pandemic.” More importantly, internal communications help seamless working and communicating abilities and help employee develop and maintain relationships and motivations with managers and other employees. Therefore, internal communications also play an important role in employee perceptions.
4.2.5 Theme 4: Impact of new internal communication strategies on employees
Interview 2 and 3 indicate that using new communication strategies may be challenging in the beginning because the new communication tools may be new for most of the employees and may take them time to get acquainted with the tools. Interviewee 1, however, states about the issues of using video conferencing tools like Google Meet and Zoom whereby employees may be shy to come forward and talk using videos in real-time and so may either mute or even switch off the camera. This not only affects communication but also shows the communication gap with the leaders because the leaders must ensure that their team is ready to work on new communication tools. Interviewee 1 states that “communicators or managers or leaders must provide instructing information to encourage employees and how to stay safe and others. Governments and major media outlets first focused on clear, simple instructions about physical distancing and lockdown guidelines.” For instance, if DXG focused on new operational rules the managers and leaders were responsible to ensure that all employees of the company are conveyed to crucial information to employees. Communicators mainly leaders and managers need to ensure that the frequency of messages and communications must not decline and must be repeated and reinforced until results are achieved. Interviewee 2 stated that “even if the message may be irritating to its employees, pushing and engaging through repeated messages and communication ensures that the employees are working thoroughly and not loosely. The CEO and senior executives also play a role in increasing the effectiveness of these internal tools. The CEO doesn’t have to be the chief delivery officer. During a crisis, it is best if the message comes from the person viewed as an authority on the subject. For business continuity, that person may well be the CEO. But for other topics, people may prefer to hear from a health expert, the leader of the organization’s crisis-response team, or even their manager.” It is also important for the managers and leaders to convey crucial information to employees including information on health crisis, health-risk-related messages, new tasks and motivational communications to employees as well as all other stakeholders.
Chapter 5: Conclusion
5.1 Conclusion
The research aim of the study is to investigate the internal communication strategies to keep employees motivated and engaged during COVID-19. From the above discussion of the study, it has been noticed that the global pandemic situation due to coronavirus has a negative impact on the business operation of the organisation while many employees have faced issues due to this negative impact. Most of the employees working in the business firm are being laid out. Based on the understanding from the qualitative interviews, it may be stated that the pandemic situation has significantly affected the business processes like changes in business operations, layoffs, work from home structures, employee negative perceptions and others. Furthermore, it is also evident from the interviews that businesses have the capabilities to adopt new communication strategies but have to first improve the preparedness of the employees to adopt new business processes like a new communication tool. There is a significant relationship between the findings from both survey and the interviews and the internal communication strategies comprise of adoption of new communication tools and communication flexibilities like using Whatsapp, Slack and other video conferencing applications. The vulnerabilities because of the pandemic have expanded for the employees working in organisations as there have been boundless lay-offs and pay cuts from occupations across enterprises all through the world. The subject of the examination is to research the inside correspondence methodologies to keep workers spurred and connected during COVID-19. The instance of DXG has been embraced for assessing the exploration theme as the staff of the organisation had been exposed to telecommute rules. There were additional reports of low inspiration and commitment of the staff which the organisation had the option to defeat by executing powerful inner systems of correspondence. Based on these findings the researcher had made certain recommendations in the following chapter.
5.2 Research sub-questions
- What are the job security and work-related concerns of the employees due to COVID-19 and what is its effect on motivation and engagement?
The job security and work-related concern that is being faced by the employees comprise of job loss, deduction in salaries along with increased mental and physical stress. The situation of COVID-19 has imposed the situation of complete lockdown in the countries as a result of which people are suffering to maintain their livelihood. Almost all of the industries operating in the global business platform have shut down their operations as a result of which millions of people around the globe have either lost their jobs or other financial issues from losing their jobs. Potential unemployment has increased concern of financial securities as a result of which the motivation of employees is low. Poor workplace engagement has also made them uncertain about their future. Building pressure due to financial concern and family[WZ16] employees are showing signs of lack of emotion, low motivation and work engagement that impacts on their livelihood and quality of their lifestyle. Based on the interview findings, it is evident that some employees from DXG also lost their jobs and this raised concerns amongst many employees concerning job security. On the other hand, work-related concerns are mainly associated with temporary depletion of engagement and poor performance from familiarising with the new environment.
- What is the present internal communication strategy practised in DXG?
The critical information has been gathered that points out DXG business uses the top-down approach as their internal communication strategy. The face to face internal communication strategy benefits the firm in understanding the employees and develops a relationship with them. It also becomes easier for the DXG to build competencies and skills that help them to positively contribute to the growth of the organisation. Furthermore, the internal communication strategies used by DXG also help them in building the traits of empathy among the employees. Developing the behaviour of the employees benefits the firm in attracting revenue and customer footfall as employees help towards growing the reputation of the firm among their customers. DXG also uses a top-down approach as the internal communication strategy as it aids the firm in receiving feedback from the employees. Based on the feedbacks, changes and development are made that help DXG to grow their brand reputation and status.
- Which internal communication strategies are effective in motivating and encouraging the staff during COVID-19?
The study had indicated clearly that the internal communication strategies that are being used by the business firm for motivating and encouraging the staff during the COVID-19. [WZ17] The internal communication strategies comprise of using digital tools such as Google Hangouts, Zoom and Skype. The internal communication strategies aid the organisation in discussing the emergency plans that need to be implemented during the tough and challenging situation. Furthermore, the pieces of evidence gathered also reflect that the internal communication strategy used during the COVID-19 period also helps in developing peer-to-peer communication that increases employee engagement and collaboratively performs the organisational activities. Furthermore, internal communication strategies are also flexible that in how the employee manages the employees to arrange information, prioritising the activities along with growing the chances of making the business successful. Through the internal communication process, it also becomes easier for the business ventures to access feedbacks from the employees that also help in growing the competencies and capabilities of the firm.
5.3 Main research question
- What are the internal communication strategies that can be implemented to keep employees motivated and engaged during COVID-19?
Business enterprises during the global pandemic situation of COVID-19 have adopted digital internal communication strategies to maintain communication with the employees along with motivating them. Internal communication strategies increase resilience and encourage the staff to collaborate and perform with high standards to grow the productivity of the business. The situation of COVID-19 has forced the people to sit in their homes and adapt to the new normal protocols. Using the digital form of technology such as Google Hangout, Skype and video call has made it possible for the organisation to reduce the effect of COVID-19 by not gathering large crowds in the offices. It also motivates the employees to work with integrity as they are being offered flexibility, work-life balance and financial security. Through the help of internal communication, the employees also maintaining documents along with record-keeping that helps the enterprise in increasing their reputation and maintaining continuous growth.
5.4 Critical reflection
The critical reflection of chapter five has explained the current situation of COVID-19 and the strategies adopted by the organisation to perform their business activities. Throughout the section, the researcher has learned that internal communication strategies play a critical role in the growth of the firm. Digital technologies such as Google Hangout and Skype are being used as the internal communication platform that assists the firm in accessing feedback and ideas that generate high success and revenue for the business entity.
There is a scope for future research in the domain of examining the internal communication strategies applicable to organisations across the specific industries such as services and manufacturing to ensure cohesiveness among the employees. Future research can be targeted at considering the culture of nations for examining the impact of internal communication strategies for shaping the engagement and motivation of the employees.
Chapter 6: Recommendations to DXG and other similar companies facing issues from COVID-19 pandemic
In this section, recommendations to the managers of DXG have been presented based on the findings from the survey and interview. COVID-19 pandemic caused both financial and non-financial loss to the company and as a result, it not only affected the performance but also greatly impacted the motivations and engagement of the employees. In this section, certain recommendations have been made based on the understanding from the literature findings as well as the interview analysis.
The first recommendation to the company managers is that even if the company had adopted and updated their internal communication systems like Zoom, Whatsapp or Google Meet, it is important that before introduction, the managers must consult with the employees on the feasibility of using the same and develop a plan to help employees familiarise with the tools. This is the first time the employees will be using these applications and as found from the interviews, the employees face many issues like internet issues, issues from surrounding disturbances, and others. Therefore, the managers and the company management must first ensure that these applications can be used by all the employees of the company and if not, the company must look for strategies to provide with the facilities to help the employees overcome the challenges. Furthermore, the manager and company management must also ensure that technical facilities are provided to the employees working from home so that internal communication tools like Zoom, Whatsapp or Google Meet may be used efficiently. Once the tools recommended for usage by the employees are set, the HR team must ensure that there are is technical support as well as training for the employees to learn how to use these tools. So, it is also recommended that the HR may organize training sessions for employees to use these tools and keep a track record on the performance of the employees in using the applications by frequently taking feedbacks on issues faced and others.
Secondly, rolling out an internal communication newsletter where the CEO directly addresses the employees to keep them informed on the COVID-19 pandemic situation. Internal communication must not be limited to digital technologies like Zoom, Whatsapp or Google Meet, and there must be direct communication strategies as well between the employees and the top-level management. For this, the researcher has proposed an internal communication newsletter template which can be found in appendix III to keep employees informed and engaged. The newsletter template will help the managers to directly reach out to their employees that is and it will be visible through their e-mails or organisational working platforms. Managers and management can post information and updates on different project work as well as new decisions that the management is going to take and other information that every employee must be aware of. The management can assign the development of such newsletter for internal communication to the IT department whereby they can develop the same and ensure that all employees have access to the same. Furthermore, the managers can also use them to continuously motivate the employee during difficult times and increase the engagement of the employees.
DXG business uses internal communication strategies to maintain the relationship with employees. The business entity, while using the internal communications strategies, can use employee engagement metrics that help in understanding the traits of the customers. These employee engagement metrics can be assessed using the rate of absenteeism, productivity, a survey of employees, and scheduled management of the employees for completion of tasks amongst others. Besides, it will also help DXG in measuring the overall employee engagement metrics that will allow the firm to have deep insight into the activities performed by the employees. Furthermore, the employee engagement metrics will also help the firm in welcoming new ideas and suggestions from the employees that will be useful towards the growth of the business organisation. These metrics can be developed by using a scale of 0 to 10 and rate the employees over 1 month in the beginning and cross-check with the managers to validate the same as a pilot test. Once, the pilot test is successful the HR may implement the scaling system or look for a more efficient metric system. This would help the managers of DXG to calculate the effectiveness and engagement of the employees.
One of the challenges that the DXG firm might faces while carrying out the overall operations through the digital platform is their behaviour. Positive employee behaviour enables the business firm in achieving high growth, whereas employee unethical behaviour increases the challenge of poor brand identity and downgrade sales. Implementing work quality metrics will benefit the business in recording the overall activities of the employees digitally. The KPI metrics will also help in the performance evaluation of the employees along with helping them to improve their decision-making capabilities. Through the KPI metrics, it also becomes easier for the organisation to have a complete look towards the goal of the firm and motivate the employees to work accordingly. The managers may use balanced scorecards or use a KPI dashboard available for purchase like Salesforce, SAP and others. however, it is not recommended to purchase any new application keeping in mind the financial issues of DXG. However, the mangers may use and develop a KPI dashboard that records employee work progress as well as employee’s motivations and perceptions from the current situation. So, managers can give special attention to employees with poor scores and help them improve by exploring the issues and challenges and mitigating them. The KPIs like communication efficiency and accuracy of the information can be used as a metric for making improvements in the internal communications strategy of the company. This would increase the effectiveness of communication to reduce the sense of loneliness and counter the diminishing productivity of the employees.
Reference list
Albrecht, S., Bakker, A., Gruman, J., Macey, W., & Saks, A. (2015). Employee engagement, human resource management practices and competitive advantage: An integrated approach. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness. People and Performance, 1(2), 7-35.
Alfalih, A. (2020). Drivers of employee sustainable motivation on private enterprises in Saudi Arabia during the crisis of COVID-19. Management Science Letters, 11(1), 171-178.
Bachman, J., Norman, W., Hopkins, C., & Brookover, R. (2016). Examining the role of self-concept theory on motivation, satisfaction, and intent to return music festival volunteers. Event Management, 20(1), 41-52.
Bartsch, S., Weber, E., Büttgen, M., & Huber, A. (2020). Leadership matters in crisis-induced digital transformation: how to lead service employees effectively during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Service Management, 1(1), 14.
BBC. (2020). Coronavirus: The world in lockdown in maps and charts. Retrieved Oct 3, 2020, from BBC: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-52103747
Bieńkowska, A., Tworek, K., & Zabłocka-Kluczka, A. (2020). Organizational Reliability Model Verification in the Crisis Escalation Phase Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability, 12(10), 4318.
Blundell, R., Costa Dias, M., Joyce, R., & Xu, X. (2020). COVID‐19 and Inequalities. Fiscal Studies, 41(2), 291-319.
Caligiuri, P., De Cieri, H., Minbaeva, D., Verbeke, A., & Zimmermann, A. (2020). International HRM insights for navigating the COVID-19 pandemic: Implications for future research and practice. Journal of International Business Studies, 1(1), 1.
Campos, R., Arrazola, M., & de Hevia, J. (2018). Finding the right employee online: Determinants of internet recruitment in Spanish firms. Applied Economics, 1(50), 79-93.
Christina, S., Dainty, A., Daniels, K., & Waterson, P. (2014). How organisational behaviour and attitudes can impact building energy use in the UK retail environment: a theoretical framework. Architectural Engineering and Design Management, 10(1-2), 164-179.
Chumg, H., Seaton, J., Cooke, L., & Ding, W. (2016). Factors affecting employees’ knowledge-sharing behaviour in the virtual organisation from the perspectives of well-being and organisational behaviour. Computers in Human Behavior, 64, 432-448, DOI-10.1016/j.chb.2016.07.011.
Ciobotă, G. (2017). Knowledge Horizons. Economics. Internal communication marketing role within organization, 9(2), 6-9.
Dey, M., Frazis, H., Loewenstein, M., & Sun, H. (2020). Ability to work from home: evidence from two surveys and implications for the labour market in the COVID-19 pandemic. Monthly Labor Review.
Ewing, M., Men, L., & O’Neil, J. (2019). Using social media to engage employees: Insights from internal communication managers. International Journal of Strategic Communication, 13(2), 110-132.
Forsythe, E., Kahn, L., Lange, F., & Wiczer, D. (2020). Labor Demand in the time of COVID-19: Evidence from vacancy postings and UI claims. Journal of Public Economics, 189(1), 104238.
Garcia-Carbonell, N., Martin-Alcazar, F., & Sanchez-Gardey, G. (2016). 2016. The views of Spanish HR managers on the role of internal communication in translating HR strategies into HRM systems. European Management Journal, 34(3), 269-281.
Goodman, M. (2019). Introduction to the special issue: corporate communication–transformation of strategy. Journal of Business Strategy, 4-5.
Gould-Williams, J. (2016). Managers’ motives for investing in HR practices and their implications for public service motivation: a theoretical perspective. International Journal of Manpower, 37(5), 764-776.
Huczynski, A., & Buchanan, D. (2013). Organisational Behaviour (8th ed.). London: Harlow: Pearson.
Jasmine, C. (2019). Impacts of Covid-19 on Company and Efforts to Support Organization Adaptable. Dr. David F. Rico, PMP, ACP, CSM, 1(1), 67-70.
Kelley-Quon, L. (2018). Surveys: Merging qualitative and quantitative research methods. In Seminars in pediatric surgery. London: WB Saunders .
Kumar, R. ( 2019). Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. London: Sage Publications Limited.
Liu, S., & Yuan, Q. (2015). The Evolution of Information and Communication Technology in Public Administration. Public Administration And Development, 2(35), 140-151. doi: 10.1002/pad.1717.
Ma, L., & Zhan, M. (2016). Effects of attributed responsibility and response strategies on organizational reputation: A meta-analysis of situational crisis communication theory research. Journal of Public Relations Research, 28(2), 102-119.
Marcua, N., & Meghisanb, G. (2015). Marketing culture and employee responsibility influence on mobile telecommunications companies’ turnover. Procedia Economics and Finance, 1(22), 277-281.
Mellinger, C., & Hanson, T. (2016). Quantitative research methods in translation and interpreting studies. London: Taylor & Francis.
Menges, J., Tussing, D., Wihler, A., & Grant, A. (2017). When job performance is all relative: how family motivation energizes effort and compensates for intrinsic motivation. Academy of Management Journal, 60(2), 695-719.
Meske, C., Kissmer, T., & Stieglitz, S. (2018). Global adoption of unified communication technologies as part of digital transformation in organizations: A cross-cultural perspective. Proceedings of the 10th Multikonferenz Wirtschaftsinformatik (MKWI), 133-144.
Mullins, L. J. (2016). Management & organisational behaviour (Eleventh Edition ed.). Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall.
Murphy, M. (2017). Internal Strategies for Assessing Communication Channel Effectiveness, 1(2), 8.
Neto, M., da Silva, L., & Ferreira, C. ( 2018). Influence of Internal Communication on the Organizations’ Performance: Proposition of Model. Future Studies Research Journal: Trends and Strategies, 10(2), 214-237.
Ozkeser, B. (2019). Impact of training on employee motivation in human resources management. Procedia Computer Science, 1(158), 802-810.
Quaratino, L., & Mazzei, A. ( 2018). Managerial strategies to promote employee brand consistent behavior. EuroMed Journal of Business, 3(1), 8.
Quirke, B. (2017). Making the connections: using internal communication to turn strategy into action (2nd ed.). London: Routledge.
Rollinson, D. (2008). Organisational Behaviour and Analysis: An Integrated Approach (4th ed.). London: London: Pearson, ISBN-978-0273711148.
Saunders, M. (2011). Research methods for business students (2nd ed.). London: Pearson Education.
Sembiring, M., Fatihudin, D., Mochklas, M., & Holisin, I. (2020). Banking Employee Performance During Pandemic Covid-19: Remuneration And Motivation. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology, 12(1), 64-71.
Shankar, K. (2020). The impact of COVID‐19 on IT services industry‐expected transformations. British Journal of Management, 31(3), 450.
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 104(8), 333-339.
Taherdoost, H. (2017). Determining sample size; how to calculate survey sample size. International Journal of Economics and Management Systems, 2(1), 2.
Venkatesh, V. (2020). Impacts of COVID-19: A research agenda to support people in their fight. International Journal of Information Management, 1(1), 102197.
Williams, C. (2011). Research methods. Journal of Business & Economics Research (JBER), 5(3), 22.
Wolterskluwer. (2020). Digital eXperience Group. Retrieved Oct 3, 2020, from https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/about-us/organization
Appendix-I (survey)
- Demography and General description
- Gender
Male
Female
- Age
Less than 25 years
25-44
More than 44 years
- Years of Experience
Less than 5 years
5-10 years
More than 10 years
- Educational Qualification
Graduate/Postgraduate
Certificate/Diploma
PhD
Others
- COVID-19 impacted your job security perceptions
Yes
No
Not sure
- COVID-19 concerned you with health impacts
Yes
No
Not sure
- Did the company have internal communication systems before COVID-19?
Yes
No
Not sure
- During COVID-19 any new internal communication method was used?
Yes
No
Not sure
- Which of the following communication tools did you use?
Email (Google, Outlook etc)
Instant messaging (Slack, Whatsapp, Hangouts etc)
Video conferencing tools (Zoom, Skype etc)
Others
APPENDIX-II (interview guide)
Q1. Gender
Q2. Department
Q3. Designation
Q4. How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the business operations of DGX? Please elaborate.
Q5. Has the COVID-19 pandemic brought positive or negative changes in the DGX operations? How?
Q6. How have changes in business operations affected the employee’s motivations?
Q7. What do you think the employees are coping with the changes in the company as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Q8. Did DGX adopt new communication strategies or upgrade as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic? What are the changes in communication strategies?
Q9. Do you think the new communication strategies have impacted the motivations of employees? How?
Appendix-III Interview transcripts
Transcript Interviewee 1
Q1. Gender: Male
Q2. Department: Project management team
Q3. Designation: Project schedule manager
Q4. How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the business operations of DGX? Please elaborate
Well… ummmm…. Change of business environment like people are now working from home, people talk over video conferencing, lack of tracking of employee performance, a company working virtually and dealing with customers and suppliers virtually are observed due to corona. It had also affected our business operations in the first few months of lockdown. Initially, due to lockdown, we were not able to complete our tasks and since the decision was taken suddenly many of the team members were not prepared and so many projects were on hold during the process.
Q5. Has the COVID-19 pandemic brought positive or negative changes in the DGX operations? How?
Yes, both positive and negative changes. Many employees were now able to give more time to families and this pandemic situation created a new resilience amongst the team. However, some of the employees were also laid off due to poor performance of the business and financial issues… Ummm…. Again there were also complaints from the employees for internet issues and lack of working environment was not helping the performance. SO, as a result of new work from home, many employees complained about poor internet affecting work performance, communication gaps with managers. The WFH mode is helping DXG in keeping their operations going, in a limited way. Even though there are many positives and negatives aspects of work from the home concept as during this COVID-19 crisis, people working on WFH, are compelled to live in social isolation and emotional distancing. One can balance the responsibilities of work-life domains, especially when the life domain needs as much attention as to work, during these difficult times
Q6. How have changes in business operations affected the employee’s motivations?
Ummm… I don’t know exactly but I feel that as a result of new work from home many employees complained about poor internet affecting work performance, communication gaps with managers because of the flexibility of work and others. It brought significant pain and hardship to workers for the company DXG. With redundancies and business closures, and widespread disruption even within ‘safe’ jobs, employees are having a difficult time including DXG.
Q7. What do you think the employees are coping with the changes in the company as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Ummm… not exactly but I believe, in the beginning, they may have issues of installing and other technical issues and they may have fears of layoffs and fear of infection and family health, disrupted the timing of work and other daily work, work-life imbalance, internet and telecommunication issues.
Q8. Did DGX adopt new communication strategies or upgrade as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic? What are the changes in communication strategies?
Yes… we adopted Slack, an internal communication tool that is both safe and cloud-based, e-mail already being used and Google Meet for video conferences. With the help of Slack, we can send updates and reports easily in a safe method and all files are stored in the cloud even if the receiver is not able to retrieve information at the time, and we have used the premium version where we can send over millions of messages and files and store thousands of GBs of files secured
Q9. Do you think the new communication strategies have impacted the motivations of employees? How?
Yes they have motivated, I guess… but not in the beginning. In the beginning, they may have issued challenges of salary tensions, salary delayed so employees may be worried. Some employees were delayed off so job security may be affected. Other factors such as poor employee motivations, virus infection-related worrisome, employee engagement was low at one point. Communicators or managers or leaders must provide instructing information to encourage employees and how to stay safe and others. Governments and major media outlets first focused on clear, simple instructions about physical distancing and lockdown guidelines
Transcript 2
Q1. Gender: Male
Q2. Department: Project management
Q3. Designation: Project management: team lead
Q4. How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the business operations of DGX? Please elaborate.
Oh, that virus has greatly affected us. First, we had to shut down the operations for a month or so and then we were also unsure when the lockdown will get over and there were fears of financial losses and we were already starting to lose because the expenditures were constant with no income. We also lost many good employees due to financial loss and our clients were demanding their tasks but with the sudden lockdown, we were unprepared to work from home but gradually we were able to change the situation and started to follow the guidelines set by the government and then allow the employees to work from home. Thus, many things have to change such as the HR policies, working environment and so many others. COVID-19 pandemic is likely to lead to the permanent shut down of many businesses, but not DXG though, [as they are] unable to bear the financial losses and disruptions caused by the pandemic. To get over the current situation, DXG is trying to run offices and administration jobs through the ‘Work from Home’ mode. DXG trying to cope up with the economic turbulence caused due to the COVID-19 through the usage of disruptive technology by working from home concept
Q5. Has the COVID-19 pandemic brought positive or negative changes in the DGX operations? How?
To be specific, this pandemic has brought both positive and negative changes like we had to lay off some of the middle and low-level employees that were not immediately associated with any of the ongoing projects, and there were also gaps in communication which as a result may have caused some employee to rethink and ask if their jobs were safe. So there were both positive and negative aspects, I will start with positive and these were Ummm.. flexibility for working, employees could work on their own time, women employees were given for flexibility. Plus many employees were not laid off so this is also positive. But the negatives are more like employee communication internet issues for employees, employees were not familiar with the concept “work from home” and so had issues of managing time like giving time to their kids and family as well as the same time to work or the disturbance while working.
Q6. How have changes in business operations affected the employee’s motivations?
Not sure about motivations as we did not measure them yet but I think some were bad because of the fears of layoff because their colleagues some were laid off during the period. Other factors such as the mental stress of the pandemic situation, worry about health and infections and also about their salary etc may have affected their motivations.
Q7. What do you think the employees are coping with the changes in the company as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Mostly I can relate them to fears of layoffs, fears of pay cut or no salary, challenges of working at homes with family and kids around and difficulty communicating with managers and teams. They were not even able to cope with the changes because they did not have good internet connections, family around it was difficult to make calls and video calls, also issues with the new working environment and so on. Some also did not have computers or laptops so they had to buy new or borrow from someone to work from home.
Q8. Did DGX adopt new communication strategies or upgrade as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic? What are the changes in communication strategies?
Yes, a lot, like we allowed using WhatsApp to send files and make calls, and the HR team also acquired Slack tool for securing internal communications and send images files and others. However, we already had the options of e-mails and using the Dropbox website for sharing files some of the teams were innovative to use Google teams to maintain privacy within the team and also send direct messages and emails to team leads through WhatsApp or Slack. Even if the message may be irritating to its employees, pushing and engaging through repeated messages and communication ensures that the employees are working thoroughly and not loosely. The CEO and senior executives also play a role in increasing the effectiveness of these internal tools. The CEO doesn’t have to be the chief delivery officer. During a crisis, it is best if the message comes from the person viewed as an authority on the subject. For business continuity, that person may well be the CEO. But for other topics, people may prefer to hear from a health expert, the leader of the organization’s crisis-response team, or even their manager
Q9. Do you think the new communication strategies have impacted the motivations of employees? How?
I feel that new communication strategies may be challenging in the beginning because the new communication tools may be new for most of the employees and may take time to get acquitted with the tools. We hope that the new normal will appear soon and will need time to get acquainted with the work from home concept. Digital channels such as enterprise social media, on-demand or live stream videos, and tele-conferencing used in employee communication and engagement, or examine relevant issues such as employee boundary management, role conflict, and innovation and creativity in the technology-mediated environment during the COVID-19 pandemic
Transcript 3
Q1. Gender: Male
Q2. Department: IT department
Q3. Designation: Assistant Manager
Q4. How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the business operations of DGX? Please elaborate.
Many changes, Ummm… To start with, financial and operational challenges increased and affected the entire business operations, the company was closed for a month or so, and then again we had to adopt digital and virtual methods of operation so that the ongoing projects can be completed. Afterwards again, we needed to embrace advanced and virtual strategies for activity with the goal that the progressing tasks can be finished.
Q5. Has the COVID-19 pandemic brought positive or negative changes in the DGX operations? How?
I would say both positive and negative, the negatives were layoffs, employee communication due to the fact they were working from home and internet issues for employees. The positives were employees were efficient to complete tasks faster and the flexible working environment.
Q6. How have changes in business operations affected the employee’s motivations?
I feel these motivations were affected by many factors such as salary delayed or no salary at all. Even some employees were delayed off so job security may be affected, poor employee motivations, virus infection-related worrisome, employee engagement were low at one point and so motivations may have decreased. There were other factors also that affected motivation and they are employee trust affected, the gap between team leads and teams, employee engagement decreased and reduced communications.
Q7. What do you think the employees are coping with the changes in the company as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic?
I think they are coping this situation moderately because they have to deal with fears of layoffs, fears of pay cut or no salary, challenges of working at homes with family and kids around, difficulty communicating with managers and teams, fear of infection and family health, disrupted the timing of work and other daily work, work-life imbalance and internet and telecommunication issues. Many parents are also working their paid jobs from home, while others have heightened financial concerns due to losing their job, and yet others involved in healthcare may be living away from their families to reduce exposing them to the virus also in case of DXG. Whatever the circumstance, the work-family balance has become increasingly challenging. Given the impact, the COVID-19 pandemic has had on employees’ work and professional lives and business priorities overall, talent management leaders are debating whether to adjust their performance review process this year
Q8. Did DGX adopt new communication strategies or upgrade as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic? What are the changes in communication strategies?
Yes, many changes were brought. Earlier the company did not allow sharing files through WhatsApp now employees can share messages and can get replies instantly plus our team and HR together taught the Slack tool for internal communications and helped the employees with using ZOOM for conferences and with other technical help.
Q9. Do you think the new communication strategies have impacted the motivations of employees? How?
I think it has affected me positively but I think I need more time to get acquitted with Slack and video conferencing methods.
APPENDIX-IV Newsletter template
| Message to all DXG employees Dear DXG Colleagues, Body text 1 Body text 2 Body text 3 Call to Action Sincerely, XYZ This message was intended for DXG employees. For internal use only ©Wolters Kluwer |






